Bed Bugs: appearance, life cycle, and treatment
Bed bugs are small parasitic insects that feed on human blood. They typically feed at night and can leave you with itchy red marks or bumps. They're found worldwide and usually live in or near where a person sleeps, including mattresses, box springs, bed frames, headboards, couches, reclining chairs, and personal mobility equipment.
But what exactly are bed bugs? How do you identify them, where do they live, and what should you do if you suspect you have a bed bug infestation? Read on to learn more.
What do bed bugs look like?
Being able to identify bed bugs can help you determine if they're the pests inside your home. Adult bed bugs are usually between a quarter inch and 3/16 of an inch long or about the size of an apple seed. Bed bugs don't have any wings, and they cannot fly or jump. Their bodies are thin, oval‐shaped, and brown or reddish‐brown. Bed bugs are also very flat, which allows them to squeeze in tight places.
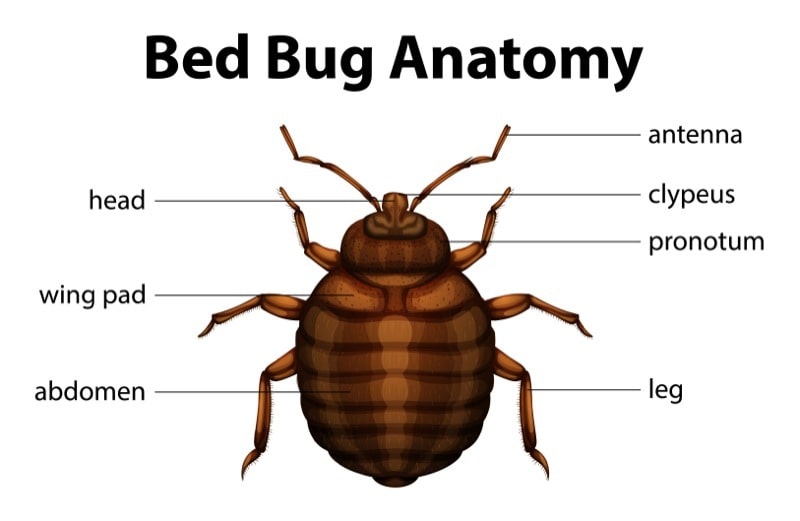
The life cycle and biology of bed bugs
Bed bugs undergo a simple life cycle with three main stages: egg, nymph, and adult.
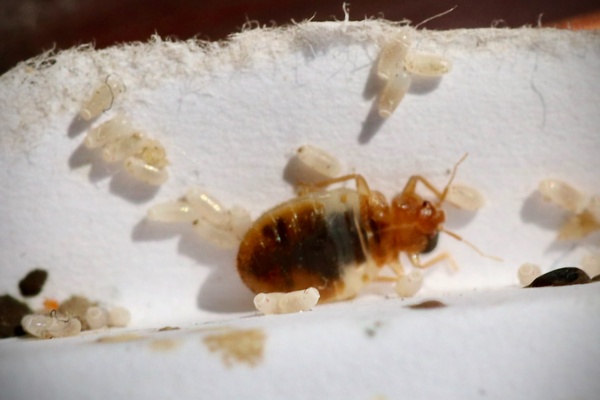
- Eggs: Bed bug eggs are tiny (about the size of a pinhead) and are typically white or translucent. Female bed bugs lay eggs in clusters and can lay around 100 eggs in their lifetime.
- Nymphs: Nymphs resemble adults but are smaller and lighter in color. They must feed on blood to molt and progress through five nymphal stages.
- Adults: Adult bed bugs can live several months to over a year, depending on factors such as temperature, availability of food (blood), and environmental conditions. This life cycle from egg to adult typically takes about 37 days under optimal conditions.
There are around 90 known bed bug species bed bug species. Luckily, only three of them are known to feed on human blood: Cimex lectularius, Cimex hemipterus, and Leptocimex boueti. The most common type of bed bug is Cimex lectularius. This bed bug is found worldwide and is the species most associated with infestations in human dwellings.
Bed bug feeding habits
What are bed bugs attracted to, and how do they find their host? Bed bugs are nocturnal insects that primarily feed on the blood of humans, although they may also bite animals if humans are not available. They are attracted to warmth, carbon dioxide, and our chemical signature “scent,” which is why they often bite humans while they sleep. After feeding, they usually retreat to their hiding places.
Where do bed bugs live?
Bed bugs primarily live in human dwellings, bird nests, and bat caves. These areas provide warmth, many hiding spots, and hosts to feed on. In homes, hotels, and other structures, they're commonly found in and around:
- Beds, mattresses, box springs, bed frames, and headboards
- Nearby furniture
- Cracks and crevices in walls, floors, baseboards, and carpeting
- Electrical outlets
- Behind wallpaper
- In luggage or other items near sleeping areas
Any small, dark, and secluded space near where people sleep or rest can be a hiding spot for bed bugs.
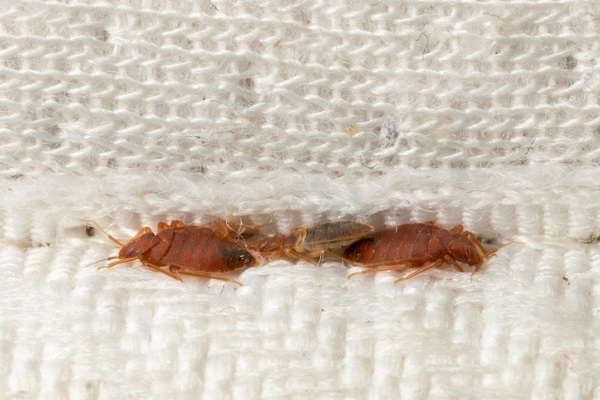

What causes bed bugs?
Bed bugs are typically spread through human activity, such as traveling, bringing infested items into homes, or moving to new residences. As expert hitchhikers, bed bugs latch onto clothing, shoes, or luggage during travel.
Living in apartments or housing units with shared walls can increase the risk of bed bug infestations. These tiny pests can easily travel between units through small cracks and remain concealed until feeding time. High‐density residences and frequently visited places like hotels and taxis also serve as transportation hubs for bed bugs.
Signs of bed bugs
The most common signs of bed bugs include:
- Small dark spots, stains, or smears from bed bug excrement on walls, bedding, bed frames, mattresses, or other furniture
- Blood stains on bedding or clothing from bed bug bites
- Shed exoskeletons
- Tiny eggs or eggshells may be found in crevices, along mattress seams, and in any harborage
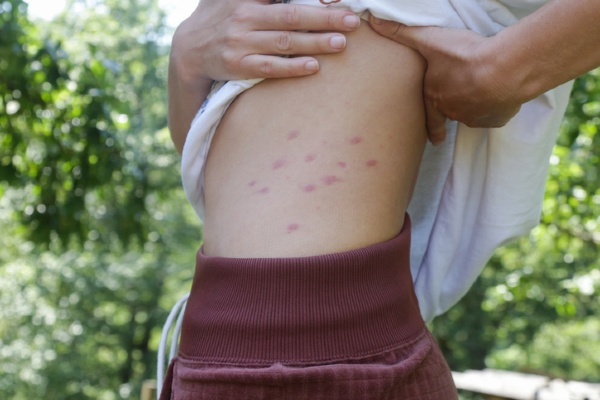
- Red, itchy welts or bites on the skin, often in a line. However, bites alone will not confirm a bed bug infestation but could bring attention that an inspection is needed
To check for bed bugs, you can:
- Inspect your mattress, box spring, and bedding for signs of bed bugs, such as reddish‐brown stains, dark spots, or shed skins
- Look for live bed bugs, especially in seams, tufts, and folds of mattresses and furniture
- Check behind headboards, along baseboards, and in cracks and crevices around the bed and nearby furniture

Bed bug bites and symptoms
Bed bug bites typically appear as small, red welts in zigzag lines or clusters on the skin. They may cause itching, irritation, and discomfort. Some people may not have any reaction to the bites. Bed bug bites can resemble bites from other insects. Check for other signs of bed bug activity to confirm their presence. While bed bugs are not known to transmit diseases, their presence can significantly disrupt daily life and cause stress.
How to get rid of and prevent bed bugs
To help prevent bed bugs, try these tips:
- Regularly inspect for signs of bed bugs, such as blood stains on sheets, mattress seams, and dark spots.
- When traveling, inspect hotel rooms for signs of bed bugs before settling in, and keep luggage elevated and away from the bed and walls.
- Seal cracks and crevices in walls, baseboards, and other potential entry points for bed bugs.
- Consider professional pest control services for regular inspections and treatments to prevent bed bug infestations.
If you see bed bugs:
- Quarantine the infested area: Avoid moving items from the infested area to other parts of your home.
- Use a vacuum cleaner with a brush attachment to remove bed bugs, eggs, and shed skins from mattresses, box springs, carpets, and furniture. Dispose of the vacuum bag or empty the canister into a sealed plastic bag immediately after vacuuming.
- Wash bedding, clothing, curtains, and other fabric items. Place items in the dryer on the highest heat setting to kill bed bugs and their eggs before washing. Bed bugs can potentially survive in the washing machine. Wash items in hot water (at least 130°F).
- Consult a pest control professional to assess the extent of the bed bug infestation and develop an effective treatment plan to eliminate bed bugs from your home.
The best way to get rid of bed bugs is to contact a professional. DIY attempts to remove bed bugs are ineffective and can worsen your situation. Terminix's bed bug control services begin with a thorough inspection. Our technicians will create a comprehensive treatment plan that eliminates bed bugs in all life stages and helps prevent them from returning. Schedule a bed bug inspection with us today!
